📘 Introduction
Welcome to our SAP RAP Tutorial and ABAP Development Guide for SAP RAP on Mastering ABAP RAP.
When developing applications using the ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP), maintaining consistent and meaningful naming conventions is crucial. SAP RAP promotes a structured approach to naming development objects, which enhances readability, maintainability, and collaboration across teams.
In this blog, we’ll explore the standard naming conventions used in RAP development and how they help streamline your ABAP projects.
If you want to familiarize yourself with ABAP RAP, you can check our blogs on SAP RAP Tutorial – ABAP RAP Business Objects: Mastering Composition vs. Association or Mastering ABAP RAP: Your Guide to SAP’s Modern Development Model to get an introduction.
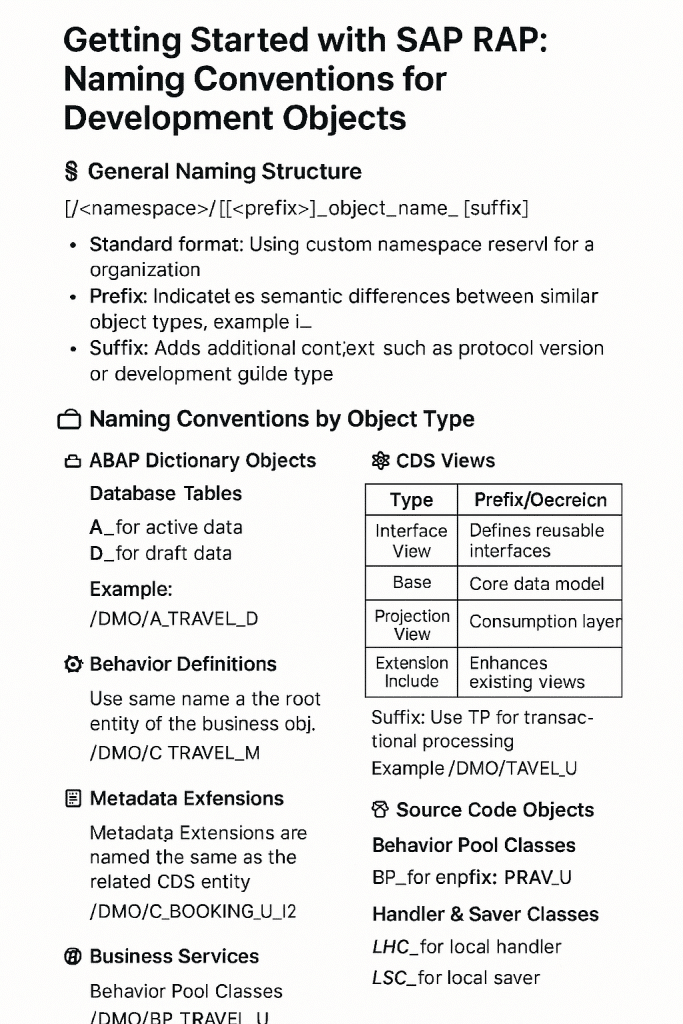
🧩 General Naming Structure
The standard format for naming development objects in RAP is:
[/<namespace>/][<prefix>]_object_name_[<suffix>]
Namespace
- Use a custom namespace reserved for your organization.
- Avoid using
/DMO/, which is reserved for demo purposes.
Prefix
- Indicates semantic differences between similar object types.
- Example:
UI_for UI service bindings,API_for Web APIs.
Suffix
- Adds additional context, such as protocol version or development guide type.
- Example:
_O2for OData V2,_Mfor managed scenario.
🗂️ Naming Conventions by Object Type : SAP RAP Tutorial
📁 ABAP Dictionary Objects
Database Tables
A_for active dataD_for draft data
Example:/DMO/A_TRAVEL_D
📄 CDS Views
| Type | Prefix | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface View | I_ | Defines reusable interfaces |
| Base View | R_ | Core data model |
| Projection View | C_ | Consumption layer |
| Extension Include | E_ | Enhances existing views |
Suffix: Use TP for transactional processing
Example: /DMO/R_AGENCYTP, /DMO/C_Travel_Processor_M
⚙️ Behavior Definitions
- Same name as the root entity of the business object
Example:/DMO/C_TRAVEL_M
🧾 Metadata Extensions
- Same name as the related CDS entity
- Use numbered suffixes for multiple extensions
Example:/DMO/C_BOOKING_U_M2
🌐 Business Services
Service Definitions
- Typically no prefix/suffix unless reused for both UI and API
Example:/DMO/TRAVEL_U,/DMO/UI_TRAVEL_U
Service Bindings
- Prefix:
UI_orAPI_ - Suffix:
_O2or_O4for OData versions
Example:/DMO/UI_TRAVEL_U_O2
🧑💻 Source Code Objects
Behavior Pool Classes
- Prefix:
BP_
Example:/DMO/BP_TRAVEL_U
Handler & Saver Classes
- Prefixes:
LHC_for local handlerLSC_for local saver
Example:LHC_TRAVEL_CREATE,LHC_BOOKING_CUD
✅ Best Practices : For SAP RAP Tutorial and Beyond
- Stick to consistent naming across all layers of your RAP application.
- Use semantic prefixes and suffixes to clarify object roles.
- Avoid using demo namespaces in production environments.
- Align naming with the development guide type (e.g.,
_R,_M,_D,_U,_C).
📌 Conclusion
Following SAP RAP naming conventions ensures your ABAP applications are clean, scalable, and easy to maintain. Whether you’re building transactional apps, APIs, or Fiori UIs, these guidelines help you stay organized and aligned with SAP best practices. Going forward in our SAP RAP tutorial we will try to stick to these conventions.
Read the next tutorial – SAP RAP Tutorial: Understanding the ABAP Flight Reference Model

Youe post is very helpful,please share step by step rap tutorial
Thank you so much! I’m really glad you found the post helpful. Absolutely—I’ll be sharing a step-by-step RAP tutorial soon to make it easier for everyone to follow along and build confidently. Stay tuned!